Last revision May 29, 2009
This page shows how to connect to file shares on the School of Earth Sciences file server, sesfs.stanford.edu, from a Windows PC on which you have logged in with a local computer account.
If you login to your PC with a Stanford Windows domain account (SUNet ID). you must follow the instructions for PC Windows domain account connection to sesfs.
General requirements for connecting to this server, including how to tell what type of account login you are using, are found on the Windows connections to sesfs page.
If you need help making the connection to sesfs.stanford.edu, put in a request on the HelpSU web site.
If you login to your PC with a local computer account, your computer does not obtain any Windows kerberos "tickets" (credentials) that can be used to authenticate you to the file server. Therefore, you must use an alternate authentication method called "NTLM".
Only version 2 of the NTLM authentication protocol is accepted by sesfs.stanford.edu. Previous versions use extremely weak (or no) encryption for your password which makes it vulnerable to capture by hackers.
In order to connect to sesfs.stanford.edu, a "local security setting" must be made on your PC to force use of an authentication level called "Send NTLMv2 response only\refuse LM & NTLM". If your PC has been joined to the Stanford Windows domain, it has the correct setting already, even though you are now using a local computer account.
If your PC has not been joined to the Stanford Windows domain, it is possible that its local security authentication level is not correct, and connection attempts to sesfs.stanford.edu will fail.
The procedure for checking and setting the NTLMv2 authentication level is highly complex. Furthermore, it can affect how you connect to other PCs and servers. Try to connect to the special share named testlogin on the sesfs.stanford.edu server using the procedure described below. Every SUNet ID has permission to connect to that share to test login procedures. If the connection to the testlogin share fails, then the problem is not permissions but most likely your authentication level setting. In that case, request help from our CRC desktop consultants using the form at the HelpSU web site. Please put the phrase "need NTLMv2 setting to connect to sesfs file server in Windows domain" in your request.
You need to know the name of the share you want to use. You can repeat this procedure to connect to multiple shares at once.
All standard methods for connecting to a Windows file server will work for sesfs.stanford.edu. The recommended method, shown below, is to map a network drive. The file share is assigned a drive letter on Windows and is available throughout the life of your login session.
The screenshots were made on Windows XP, but the process is similar for later versions of Windows.
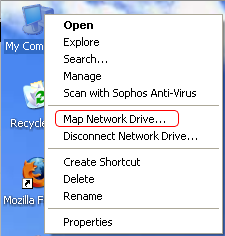
Right-click on the My Computer icon on the desktop to reveal this contextual menu:

If you don't have the My Computer icon on your desktop, you can also open the Start menu and right-click on the My Computer item there.
Select the Map Network Drive... item from the contextual menu. In the Map Network Drive window that opens, you must select a letter from the drop-down Drive: menu. You must type in the server and share specification in the Folder: field in this format:
\\sesfs.stanford.edu\sharename
substituting the name of the share you want to access for sharename. The Browse... button is not useful - none of the shares on sesfs.stanford.edu is visible when you browse the network.
In the example screenshot below, I have selected the drive letter H: and the home share farrell. When connecting from the Stanford campus network, you can abbreviate the server name by omitting the .stanford.edu domain part.
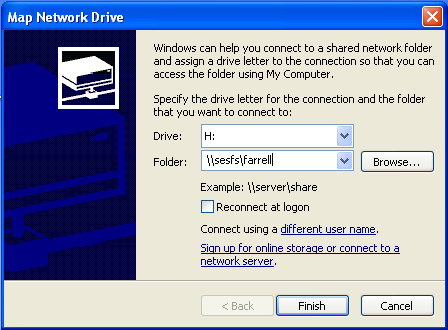
Click on the Finish button on the bottom of the window to connect to the share you have specified. You should immediately see this attempting connection window:
This should be followed right away by a login prompt window:
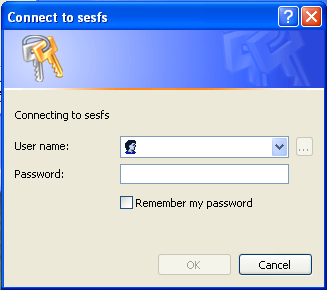
You must supply your SUNet ID name and password. But there is a trick! If you just supply your SUNet ID name in the User name: field, that will be passed to sesfs.stanford.edu to be compared to the list of local accounts on the file server. But there are no local accounts on sesfs.stanford.edu! The file server uses the accounts (SUNet IDs) that are already stored in the "Active Directory" of the Windows domain. Therefore, you have to tell the file server to compare your account name to that Active Directory. You do this by prefixing your SUNet ID name with WIN\ as shown in this screenshot:
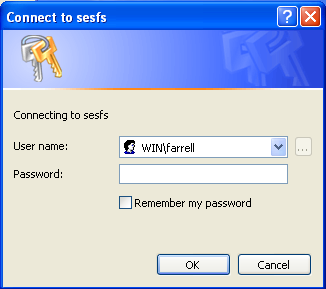
There is no space between the WIN\ domain identifier and your SUNet ID name. Type your SUNet ID password in the Password: field and then click on the OK button.
After only a few seconds, a Windows Explorer window should open to show the contents of the share, as shown in this example screenshot:
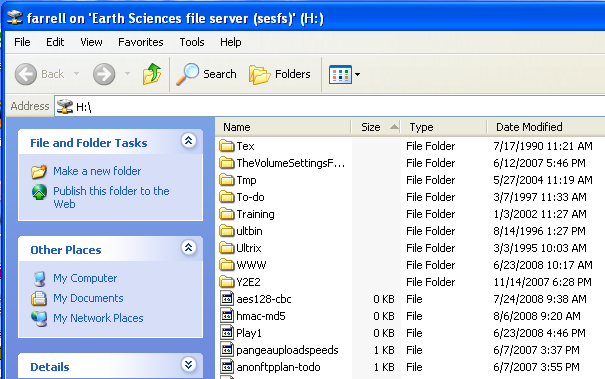
If a Windows Explorer window does not open to show the share contents, and instead you are prompted again to enter a username and password, verify that you have included the WIN\ domain identifier prefix in the name field with your SUNet ID name, and have typed the correct SUNet ID password. If it still fails, and you know that your authentication level is correctly set to NTLMv2 (see above), it is likely that your SUNet ID does not have permission to access this share. If you believe you should have access to this share, contact the system managers.
You can work with the files on this file share as if they were locally connected to your PC. Because the file share is mapped to a drive letter, if you close the Windows Explorer window, you do not lose access. Just open My Computer and click on the drive letter you selected to see the share contents again.
When you logoff or shutdown your PC, you will be automatically disconnected from the file server. You can also disconnect a file share while you stay logged in to the PC. First make sure that no program is using any file on this share, and close any Windows Explorer window that is showing its contents. Then right-click again on My Computer, but this time select Disconnect Network Drive... from the contextual menu. That will open a window showing all your connected network drives, as in this example screenshot:
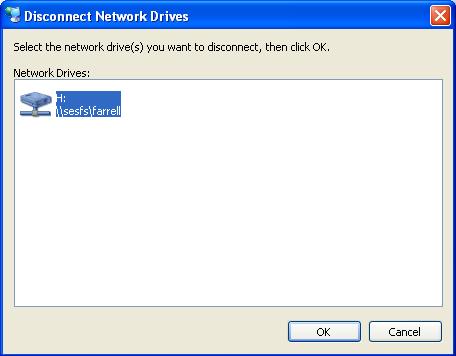
Select the drive you wish to disconnect, and click on the OK button.